注意
前往結尾以下載完整範例程式碼。或者透過 JupyterLite 或 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
視覺化股票市場結構#
此範例採用多種非監督式學習技術,從歷史報價的變化中提取股票市場結構。
我們使用的數量是每日報價價格的變化:相關的報價往往在一天的時間內相互波動。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
從網際網路檢索資料#
資料來自 2003 年至 2008 年。這段期間相當平靜:(時間不會太久,我們可以取得高科技公司,並且在 2008 年崩盤之前)。這類歷史資料可以從像是 data.nasdaq.com 和 alphavantage.co 等 API 取得。
import sys
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
symbol_dict = {
"TOT": "Total",
"XOM": "Exxon",
"CVX": "Chevron",
"COP": "ConocoPhillips",
"VLO": "Valero Energy",
"MSFT": "Microsoft",
"IBM": "IBM",
"TWX": "Time Warner",
"CMCSA": "Comcast",
"CVC": "Cablevision",
"YHOO": "Yahoo",
"DELL": "Dell",
"HPQ": "HP",
"AMZN": "Amazon",
"TM": "Toyota",
"CAJ": "Canon",
"SNE": "Sony",
"F": "Ford",
"HMC": "Honda",
"NAV": "Navistar",
"NOC": "Northrop Grumman",
"BA": "Boeing",
"KO": "Coca Cola",
"MMM": "3M",
"MCD": "McDonald's",
"PEP": "Pepsi",
"K": "Kellogg",
"UN": "Unilever",
"MAR": "Marriott",
"PG": "Procter Gamble",
"CL": "Colgate-Palmolive",
"GE": "General Electrics",
"WFC": "Wells Fargo",
"JPM": "JPMorgan Chase",
"AIG": "AIG",
"AXP": "American express",
"BAC": "Bank of America",
"GS": "Goldman Sachs",
"AAPL": "Apple",
"SAP": "SAP",
"CSCO": "Cisco",
"TXN": "Texas Instruments",
"XRX": "Xerox",
"WMT": "Wal-Mart",
"HD": "Home Depot",
"GSK": "GlaxoSmithKline",
"PFE": "Pfizer",
"SNY": "Sanofi-Aventis",
"NVS": "Novartis",
"KMB": "Kimberly-Clark",
"R": "Ryder",
"GD": "General Dynamics",
"RTN": "Raytheon",
"CVS": "CVS",
"CAT": "Caterpillar",
"DD": "DuPont de Nemours",
}
symbols, names = np.array(sorted(symbol_dict.items())).T
quotes = []
for symbol in symbols:
print("Fetching quote history for %r" % symbol, file=sys.stderr)
url = (
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/scikit-learn/examples-data/"
"master/financial-data/{}.csv"
)
quotes.append(pd.read_csv(url.format(symbol)))
close_prices = np.vstack([q["close"] for q in quotes])
open_prices = np.vstack([q["open"] for q in quotes])
# The daily variations of the quotes are what carry the most information
variation = close_prices - open_prices
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AAPL')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AIG')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AMZN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('AXP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('BA')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('BAC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CAJ')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CAT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CL')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CMCSA')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('COP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CSCO')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CVC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CVS')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('CVX')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('DD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('DELL')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('F')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GE')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GS')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('GSK')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('HD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('HMC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('HPQ')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('IBM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('JPM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('K')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('KMB')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('KO')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MAR')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MCD')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MMM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('MSFT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('NAV')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('NOC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('NVS')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('PEP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('PFE')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('PG')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('R')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('RTN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('SAP')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('SNE')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('SNY')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TOT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TWX')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('TXN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('UN')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('VLO')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('WFC')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('WMT')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('XOM')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('XRX')
Fetching quote history for np.str_('YHOO')
學習圖形結構#
我們使用稀疏逆共變異數估計來找出哪些報價在其他條件下相關。具體來說,稀疏逆共變異數會給我們一個圖形,也就是連接的列表。對於每個符號,與其連接的符號都是那些有助於解釋其波動的符號。
from sklearn import covariance
alphas = np.logspace(-1.5, 1, num=10)
edge_model = covariance.GraphicalLassoCV(alphas=alphas)
# standardize the time series: using correlations rather than covariance
# former is more efficient for structure recovery
X = variation.copy().T
X /= X.std(axis=0)
edge_model.fit(X)
使用親和力傳播進行聚類#
我們使用聚類來將行為相似的報價分組在一起。在此,在 scikit-learn 中可用的各種聚類技術中,我們使用親和力傳播,因為它不會強制執行大小相等的聚類,並且可以從資料中自動選擇聚類的數量。
請注意,這與圖形給出的指示不同,因為圖形反映變數之間的條件關係,而聚類反映邊際屬性:聚類在一起的變數可以被認為在整個股票市場的層面上具有類似的影響。
from sklearn import cluster
_, labels = cluster.affinity_propagation(edge_model.covariance_, random_state=0)
n_labels = labels.max()
for i in range(n_labels + 1):
print(f"Cluster {i + 1}: {', '.join(names[labels == i])}")
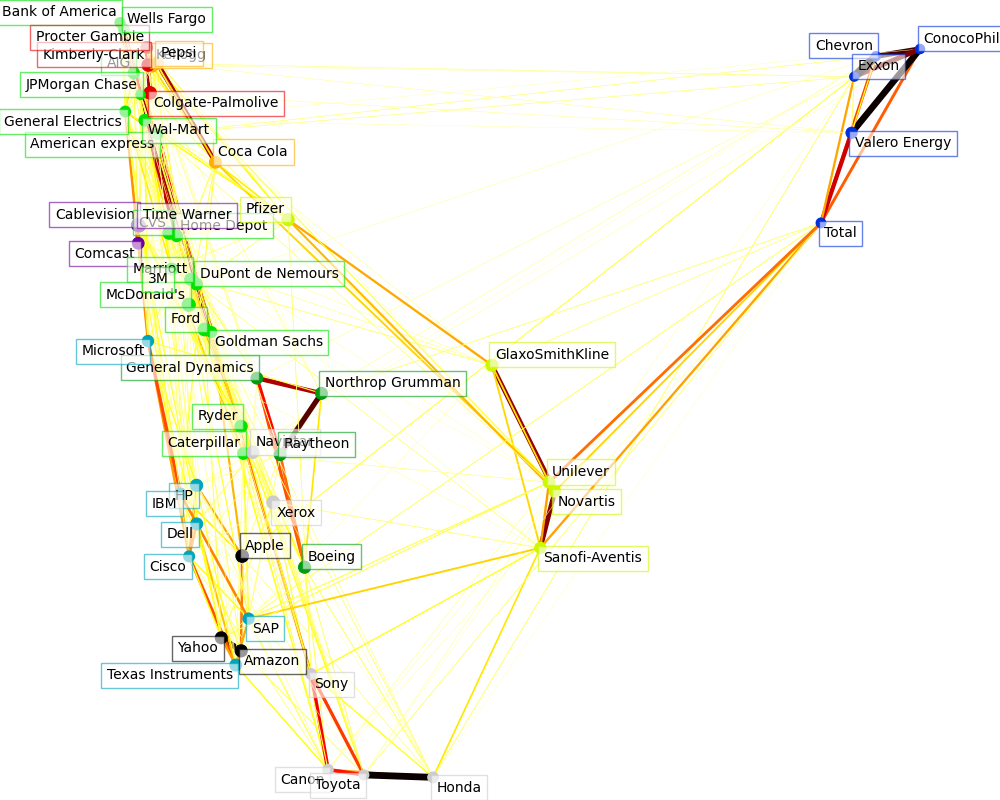
Cluster 1: Apple, Amazon, Yahoo
Cluster 2: Comcast, Cablevision, Time Warner
Cluster 3: ConocoPhillips, Chevron, Total, Valero Energy, Exxon
Cluster 4: Cisco, Dell, HP, IBM, Microsoft, SAP, Texas Instruments
Cluster 5: Boeing, General Dynamics, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon
Cluster 6: AIG, American express, Bank of America, Caterpillar, CVS, DuPont de Nemours, Ford, General Electrics, Goldman Sachs, Home Depot, JPMorgan Chase, Marriott, McDonald's, 3M, Ryder, Wells Fargo, Wal-Mart
Cluster 7: GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Unilever
Cluster 8: Kellogg, Coca Cola, Pepsi
Cluster 9: Colgate-Palmolive, Kimberly-Clark, Procter Gamble
Cluster 10: Canon, Honda, Navistar, Sony, Toyota, Xerox
嵌入到 2D 空間中#
為了視覺化,我們需要在 2D 畫布上佈置不同的符號。為此,我們使用流形學習技術來檢索 2D 嵌入。我們使用密集的 eigen_solver 來實現可重複性(arpack 是以我們無法控制的隨機向量初始化的)。此外,我們使用大量的鄰居來捕捉大規模結構。
# Finding a low-dimension embedding for visualization: find the best position of
# the nodes (the stocks) on a 2D plane
from sklearn import manifold
node_position_model = manifold.LocallyLinearEmbedding(
n_components=2, eigen_solver="dense", n_neighbors=6
)
embedding = node_position_model.fit_transform(X.T).T
視覺化#
這 3 個模型的輸出組合在 2D 圖形中,其中節點表示股票,邊表示
聚類標籤用於定義節點的顏色
稀疏共變異數模型用於顯示邊的強度
2D 嵌入用於在平面中定位節點
此範例有相當多的視覺化相關程式碼,因為視覺化對於此處顯示圖形至關重要。其中一個挑戰是定位標籤以最大限度地減少重疊。為此,我們使用基於每個軸上最近鄰的方向的啟發式方法。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
plt.figure(1, facecolor="w", figsize=(10, 8))
plt.clf()
ax = plt.axes([0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0])
plt.axis("off")
# Plot the graph of partial correlations
partial_correlations = edge_model.precision_.copy()
d = 1 / np.sqrt(np.diag(partial_correlations))
partial_correlations *= d
partial_correlations *= d[:, np.newaxis]
non_zero = np.abs(np.triu(partial_correlations, k=1)) > 0.02
# Plot the nodes using the coordinates of our embedding
plt.scatter(
embedding[0], embedding[1], s=100 * d**2, c=labels, cmap=plt.cm.nipy_spectral
)
# Plot the edges
start_idx, end_idx = np.where(non_zero)
# a sequence of (*line0*, *line1*, *line2*), where::
# linen = (x0, y0), (x1, y1), ... (xm, ym)
segments = [
[embedding[:, start], embedding[:, stop]] for start, stop in zip(start_idx, end_idx)
]
values = np.abs(partial_correlations[non_zero])
lc = LineCollection(
segments, zorder=0, cmap=plt.cm.hot_r, norm=plt.Normalize(0, 0.7 * values.max())
)
lc.set_array(values)
lc.set_linewidths(15 * values)
ax.add_collection(lc)
# Add a label to each node. The challenge here is that we want to
# position the labels to avoid overlap with other labels
for index, (name, label, (x, y)) in enumerate(zip(names, labels, embedding.T)):
dx = x - embedding[0]
dx[index] = 1
dy = y - embedding[1]
dy[index] = 1
this_dx = dx[np.argmin(np.abs(dy))]
this_dy = dy[np.argmin(np.abs(dx))]
if this_dx > 0:
horizontalalignment = "left"
x = x + 0.002
else:
horizontalalignment = "right"
x = x - 0.002
if this_dy > 0:
verticalalignment = "bottom"
y = y + 0.002
else:
verticalalignment = "top"
y = y - 0.002
plt.text(
x,
y,
name,
size=10,
horizontalalignment=horizontalalignment,
verticalalignment=verticalalignment,
bbox=dict(
facecolor="w",
edgecolor=plt.cm.nipy_spectral(label / float(n_labels)),
alpha=0.6,
),
)
plt.xlim(
embedding[0].min() - 0.15 * np.ptp(embedding[0]),
embedding[0].max() + 0.10 * np.ptp(embedding[0]),
)
plt.ylim(
embedding[1].min() - 0.03 * np.ptp(embedding[1]),
embedding[1].max() + 0.03 * np.ptp(embedding[1]),
)
plt.show()
腳本的總執行時間:(0 分鐘 2.704 秒)
相關範例