注意
跳到結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。或透過 JupyterLite 或 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
使用交叉驗證的遞迴特徵消除#
一個遞迴特徵消除 (RFE) 範例,具有使用交叉驗證自動調整選取特徵的數量。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
資料產生#
我們使用 3 個資訊豐富的特徵建立分類任務。引入 2 個額外的冗餘(即相關)特徵的效果是,選取的特徵會根據交叉驗證的摺疊而變化。其餘的特徵不具資訊性,因為它們是隨機繪製的。
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(
n_samples=500,
n_features=15,
n_informative=3,
n_redundant=2,
n_repeated=0,
n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=1,
class_sep=0.8,
random_state=0,
)
模型訓練和選取#
我們建立 RFE 物件並計算交叉驗證分數。評分策略「準確率」可最佳化正確分類樣本的比例。
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
min_features_to_select = 1 # Minimum number of features to consider
clf = LogisticRegression()
cv = StratifiedKFold(5)
rfecv = RFECV(
estimator=clf,
step=1,
cv=cv,
scoring="accuracy",
min_features_to_select=min_features_to_select,
n_jobs=2,
)
rfecv.fit(X, y)
print(f"Optimal number of features: {rfecv.n_features_}")
Optimal number of features: 3
在本例中,發現具有 3 個特徵(對應於真正的生成模型)的模型是最理想的。
繪製特徵數量與交叉驗證分數的關係圖#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
cv_results = pd.DataFrame(rfecv.cv_results_)
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel("Number of features selected")
plt.ylabel("Mean test accuracy")
plt.errorbar(
x=cv_results["n_features"],
y=cv_results["mean_test_score"],
yerr=cv_results["std_test_score"],
)
plt.title("Recursive Feature Elimination \nwith correlated features")
plt.show()
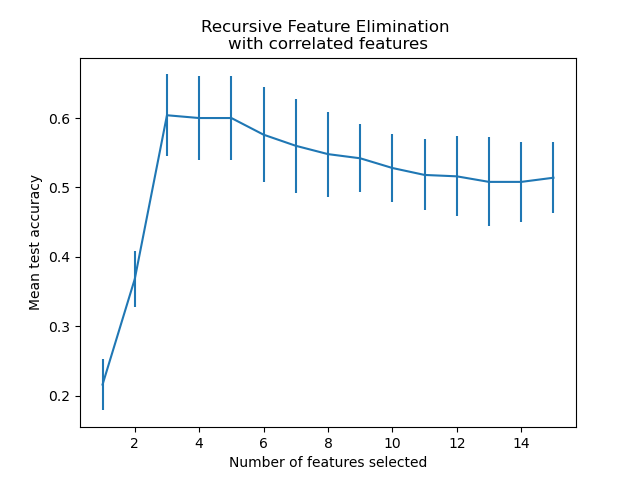
從上面的圖中,可以進一步注意到,對於 3 到 5 個選取的特徵,等效分數會出現高原期(相似的平均值和重疊的誤差線)。這是引入相關特徵的結果。實際上,RFE 選取的最佳模型可能位於此範圍內,具體取決於交叉驗證技術。測試準確性在選取 5 個以上特徵時會降低,也就是說,保留不具資訊性的特徵會導致過度擬合,因此不利於模型的統計效能。
腳本的總執行時間:(0 分鐘 0.523 秒)
相關範例