注意
前往結尾下載完整的範例程式碼。或透過 JupyterLite 或 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
混淆矩陣#
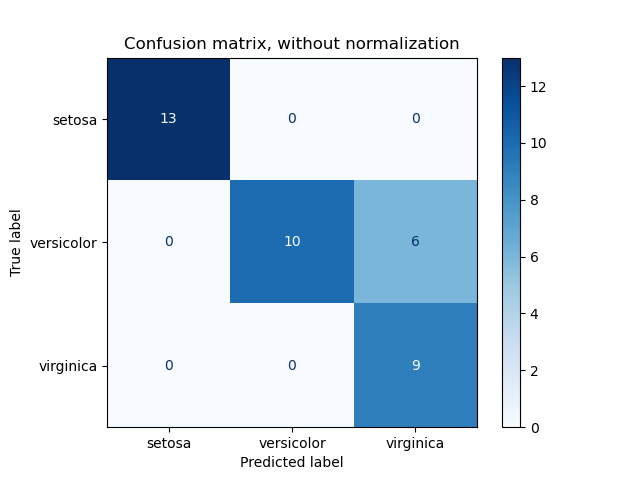
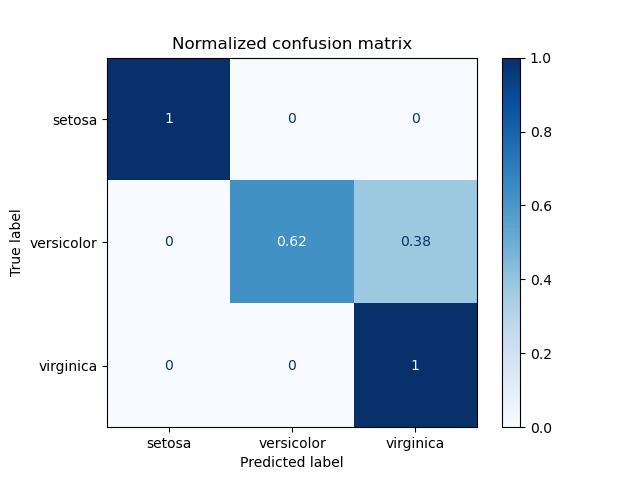
混淆矩陣使用範例,評估分類器在虹膜資料集上的輸出品質。對角線元素表示預測標籤等於真實標籤的點數,而非對角線元素是分類器錯誤標記的點數。混淆矩陣的對角線值越高越好,表示許多正確的預測。
這些圖顯示了使用和不使用類別支援大小(每個類別中的元素數量)正規化的混淆矩陣。這種正規化在類別不平衡的情況下很有趣,可以更視覺化地解釋哪個類別被錯誤分類。
這裡的結果不如預期的好,因為我們選擇的正規化參數 C 不是最好的。在實際應用中,此參數通常使用 調整估計器的超參數 來選擇。
Confusion matrix, without normalization
[[13 0 0]
[ 0 10 6]
[ 0 0 9]]
Normalized confusion matrix
[[1. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0.62 0.38]
[0. 0. 1. ]]
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets, svm
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
class_names = iris.target_names
# Split the data into a training set and a test set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
# Run classifier, using a model that is too regularized (C too low) to see
# the impact on the results
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel="linear", C=0.01).fit(X_train, y_train)
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
# Plot non-normalized confusion matrix
titles_options = [
("Confusion matrix, without normalization", None),
("Normalized confusion matrix", "true"),
]
for title, normalize in titles_options:
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay.from_estimator(
classifier,
X_test,
y_test,
display_labels=class_names,
cmap=plt.cm.Blues,
normalize=normalize,
)
disp.ax_.set_title(title)
print(title)
print(disp.confusion_matrix)
plt.show()
腳本的總執行時間: (0 分鐘 0.196 秒)
相關範例