注意
前往結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。或透過 JupyterLite 或 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
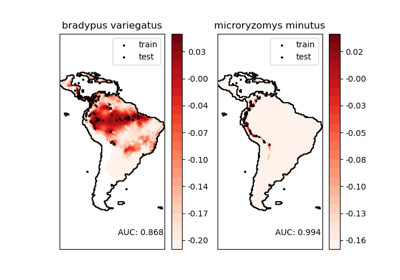
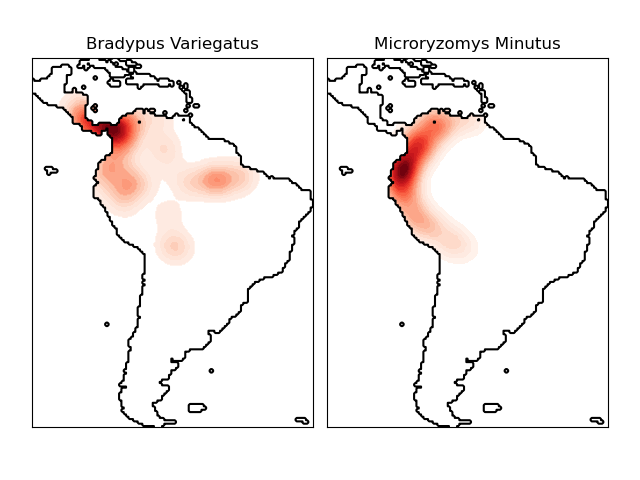
物種分佈的核密度估計#
這顯示了一個基於鄰居的查詢範例(特別是核密度估計),使用在地理空間資料上,使用基於半正矢距離度量的球樹 – 即緯度/經度上的點之間的距離。資料集由 Phillips 等人 (2006) 提供。如果可用,此範例使用 basemap 繪製南美洲的海岸線和國界。
此範例不對資料執行任何學習(請參閱 物種分佈建模,以取得基於此資料集中屬性的分類範例)。它僅顯示地理空間座標中觀察到的資料點的核密度估計。
這兩個物種是
“Bradypus variegatus”,棕喉樹懶。
“Microryzomys minutus”,也稱為森林小稻鼠,一種生活在秘魯、哥倫比亞、厄瓜多、秘魯和委內瑞拉的齧齒動物。
參考文獻#
“物種地理分佈的最大熵建模” S. J. Phillips, R. P. Anderson, R. E. Schapire - 生態建模,190:231-259, 2006。
- computing KDE in spherical coordinates
- plot coastlines from coverage
- computing KDE in spherical coordinates
- plot coastlines from coverage
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_species_distributions
from sklearn.neighbors import KernelDensity
# if basemap is available, we'll use it.
# otherwise, we'll improvise later...
try:
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
basemap = True
except ImportError:
basemap = False
def construct_grids(batch):
"""Construct the map grid from the batch object
Parameters
----------
batch : Batch object
The object returned by :func:`fetch_species_distributions`
Returns
-------
(xgrid, ygrid) : 1-D arrays
The grid corresponding to the values in batch.coverages
"""
# x,y coordinates for corner cells
xmin = batch.x_left_lower_corner + batch.grid_size
xmax = xmin + (batch.Nx * batch.grid_size)
ymin = batch.y_left_lower_corner + batch.grid_size
ymax = ymin + (batch.Ny * batch.grid_size)
# x coordinates of the grid cells
xgrid = np.arange(xmin, xmax, batch.grid_size)
# y coordinates of the grid cells
ygrid = np.arange(ymin, ymax, batch.grid_size)
return (xgrid, ygrid)
# Get matrices/arrays of species IDs and locations
data = fetch_species_distributions()
species_names = ["Bradypus Variegatus", "Microryzomys Minutus"]
Xtrain = np.vstack([data["train"]["dd lat"], data["train"]["dd long"]]).T
ytrain = np.array(
[d.decode("ascii").startswith("micro") for d in data["train"]["species"]],
dtype="int",
)
Xtrain *= np.pi / 180.0 # Convert lat/long to radians
# Set up the data grid for the contour plot
xgrid, ygrid = construct_grids(data)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(xgrid[::5], ygrid[::5][::-1])
land_reference = data.coverages[6][::5, ::5]
land_mask = (land_reference > -9999).ravel()
xy = np.vstack([Y.ravel(), X.ravel()]).T
xy = xy[land_mask]
xy *= np.pi / 180.0
# Plot map of South America with distributions of each species
fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.05, right=0.95, wspace=0.05)
for i in range(2):
plt.subplot(1, 2, i + 1)
# construct a kernel density estimate of the distribution
print(" - computing KDE in spherical coordinates")
kde = KernelDensity(
bandwidth=0.04, metric="haversine", kernel="gaussian", algorithm="ball_tree"
)
kde.fit(Xtrain[ytrain == i])
# evaluate only on the land: -9999 indicates ocean
Z = np.full(land_mask.shape[0], -9999, dtype="int")
Z[land_mask] = np.exp(kde.score_samples(xy))
Z = Z.reshape(X.shape)
# plot contours of the density
levels = np.linspace(0, Z.max(), 25)
plt.contourf(X, Y, Z, levels=levels, cmap=plt.cm.Reds)
if basemap:
print(" - plot coastlines using basemap")
m = Basemap(
projection="cyl",
llcrnrlat=Y.min(),
urcrnrlat=Y.max(),
llcrnrlon=X.min(),
urcrnrlon=X.max(),
resolution="c",
)
m.drawcoastlines()
m.drawcountries()
else:
print(" - plot coastlines from coverage")
plt.contour(
X, Y, land_reference, levels=[-9998], colors="k", linestyles="solid"
)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.title(species_names[i])
plt.show()
腳本總執行時間: (0 分鐘 3.514 秒)
相關範例