注意
跳至結尾以下載完整的範例程式碼。或透過 JupyterLite 或 Binder 在您的瀏覽器中執行此範例
目標編碼器的內部交叉擬合#
TargetEncoder 將類別特徵的每個類別替換為該類別目標變數的縮小平均值。這種方法在類別特徵和目標之間存在強烈關係的情況下非常有用。為了防止過度擬合,TargetEncoder.fit_transform 使用內部交叉擬合方案來編碼下游模型使用的訓練資料。此方案涉及將資料分割成 k 折,並使用其他 k-1 折學習的編碼來編碼每個折。在此範例中,我們展示交叉擬合程序對於防止過度擬合的重要性。
# Authors: The scikit-learn developers
# SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
建立合成資料集#
在此範例中,我們建立一個具有三個類別特徵的資料集
具有中等基數的資訊豐富特徵(「資訊豐富」)
具有中等基數的非資訊豐富特徵(「隨機」)
具有高基數的非資訊豐富特徵(「接近唯一」)
首先,我們產生資訊豐富的特徵
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import KBinsDiscretizer
n_samples = 50_000
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
y = rng.randn(n_samples)
noise = 0.5 * rng.randn(n_samples)
n_categories = 100
kbins = KBinsDiscretizer(
n_bins=n_categories,
encode="ordinal",
strategy="uniform",
random_state=rng,
subsample=None,
)
X_informative = kbins.fit_transform((y + noise).reshape(-1, 1))
# Remove the linear relationship between y and the bin index by permuting the
# values of X_informative:
permuted_categories = rng.permutation(n_categories)
X_informative = permuted_categories[X_informative.astype(np.int32)]
具有中等基數的非資訊豐富特徵是透過置換資訊豐富的特徵並移除與目標的關係來產生
X_shuffled = rng.permutation(X_informative)
產生具有高基數的非資訊豐富特徵,使其獨立於目標變數。我們將展示,在沒有交叉擬合的情況下進行目標編碼將導致下游迴歸器的災難性過度擬合。這些高基數特徵基本上是樣本的唯一識別碼,通常應從機器學習資料集中移除。在此範例中,我們產生它們是為了展示 TargetEncoder 的預設 交叉擬合 行為如何自動減輕過度擬合問題。
X_near_unique_categories = rng.choice(
int(0.9 * n_samples), size=n_samples, replace=True
).reshape(-1, 1)
最後,我們組裝資料集並執行訓練測試分割
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X = pd.DataFrame(
np.concatenate(
[X_informative, X_shuffled, X_near_unique_categories],
axis=1,
),
columns=["informative", "shuffled", "near_unique"],
)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
訓練嶺迴歸器#
在本節中,我們訓練一個具有和不具有編碼的資料集上的嶺迴歸器,並探索具有和不具有內部 交叉擬合 的目標編碼器的影響。首先,我們看到在原始特徵上訓練的嶺模型將具有較低的效能。這是因為我們置換了資訊豐富特徵的順序,這表示當為原始值時,X_informative 不會提供資訊
import sklearn
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
# Configure transformers to always output DataFrames
sklearn.set_config(transform_output="pandas")
ridge = Ridge(alpha=1e-6, solver="lsqr", fit_intercept=False)
raw_model = ridge.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Raw Model score on training set: ", raw_model.score(X_train, y_train))
print("Raw Model score on test set: ", raw_model.score(X_test, y_test))
Raw Model score on training set: 0.0049896314219659565
Raw Model score on test set: 0.004577621581492997
接下來,我們建立一個包含目標編碼器和嶺模型的管線。管線使用 TargetEncoder.fit_transform,它使用 交叉擬合。我們看到模型很好地擬合資料並推廣到測試集
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import TargetEncoder
model_with_cf = make_pipeline(TargetEncoder(random_state=0), ridge)
model_with_cf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("Model with CF on train set: ", model_with_cf.score(X_train, y_train))
print("Model with CF on test set: ", model_with_cf.score(X_test, y_test))
Model with CF on train set: 0.8000184677460305
Model with CF on test set: 0.7927845601690917
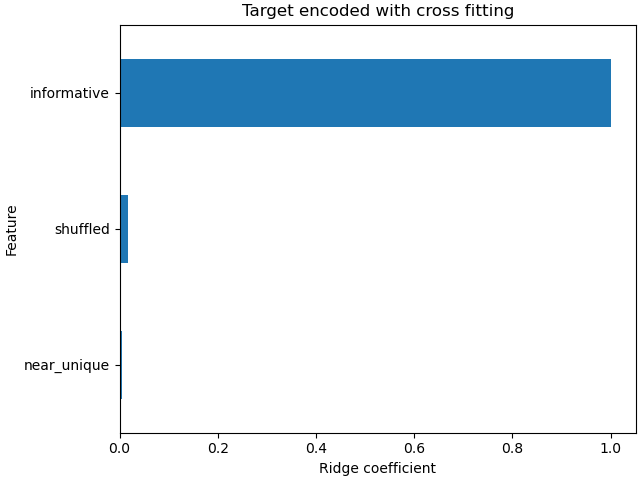
線性模型的係數顯示,大多數權重都在索引為 0 的資料行上的特徵上,這是資訊豐富的特徵
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
plt.rcParams["figure.constrained_layout.use"] = True
coefs_cf = pd.Series(
model_with_cf[-1].coef_, index=model_with_cf[-1].feature_names_in_
).sort_values()
ax = coefs_cf.plot(kind="barh")
_ = ax.set(
title="Target encoded with cross fitting",
xlabel="Ridge coefficient",
ylabel="Feature",
)
雖然 TargetEncoder.fit_transform 使用內部 交叉擬合 方案來學習訓練集的編碼,但 TargetEncoder.transform 本身則沒有。它使用完整的訓練集來學習編碼並轉換類別特徵。因此,我們可以使用 TargetEncoder.fit,然後使用 TargetEncoder.transform 來停用 交叉擬合。然後,將此編碼傳遞到嶺模型。
target_encoder = TargetEncoder(random_state=0)
target_encoder.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_train_no_cf_encoding = target_encoder.transform(X_train)
X_test_no_cf_encoding = target_encoder.transform(X_test)
model_no_cf = ridge.fit(X_train_no_cf_encoding, y_train)
我們評估在編碼時未使用 交叉擬合 的模型,並看到它過度擬合
print(
"Model without CF on training set: ",
model_no_cf.score(X_train_no_cf_encoding, y_train),
)
print(
"Model without CF on test set: ",
model_no_cf.score(
X_test_no_cf_encoding,
y_test,
),
)
Model without CF on training set: 0.858486250088675
Model without CF on test set: 0.6338211367102258
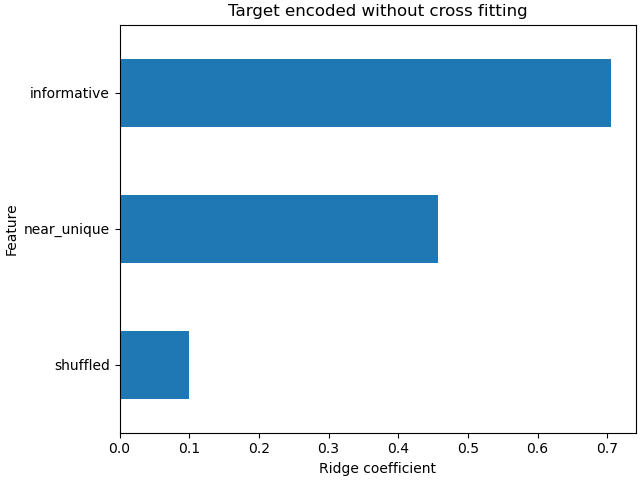
嶺模型過度擬合,因為它將比模型使用 交叉擬合 來編碼特徵時,更多的權重分配給非資訊豐富的極高基數(「接近唯一」)和中等基數(「隨機」)特徵。
coefs_no_cf = pd.Series(
model_no_cf.coef_, index=model_no_cf.feature_names_in_
).sort_values()
ax = coefs_no_cf.plot(kind="barh")
_ = ax.set(
title="Target encoded without cross fitting",
xlabel="Ridge coefficient",
ylabel="Feature",
)
結論#
此範例示範 TargetEncoder 內部 交叉擬合的重要性。在將訓練資料傳遞到機器學習模型之前,使用 TargetEncoder.fit_transform 來編碼訓練資料非常重要。當 TargetEncoder 是 Pipeline 的一部分,且管線已擬合時,管線會正確地呼叫 TargetEncoder.fit_transform,並在編碼訓練資料時使用 交叉擬合。
腳本總執行時間:(0 分鐘 0.315 秒)
相關範例