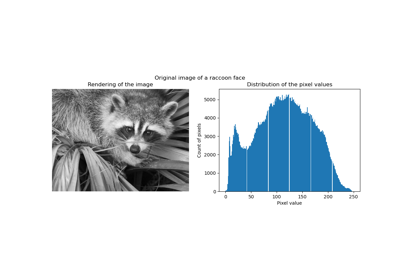
使用 K-Means 進行顏色量化#
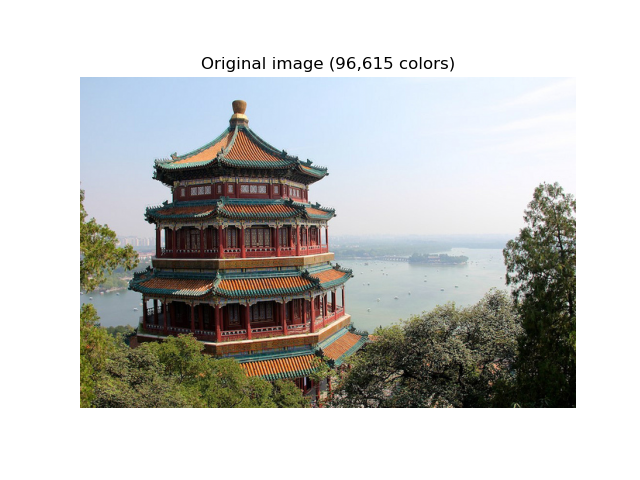
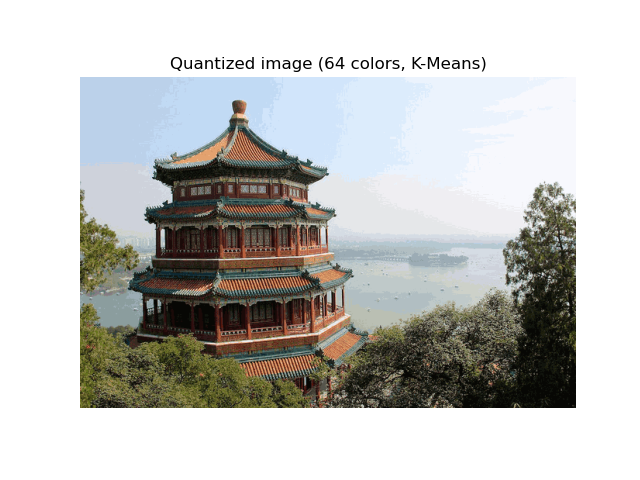
對一張頤和園(中國)的圖像執行像素級向量量化(VQ),將顯示圖像所需的顏色數量從 96,615 種獨特顏色減少到 64 種,同時保留整體外觀品質。
在本範例中,像素以 3D 空間表示,並使用 K-means 找到 64 個顏色群集。在圖像處理文獻中,從 K-means 獲得的碼本(群集中心)稱為色盤。使用單個位元組,最多可以處理 256 種顏色,而 RGB 編碼每個像素需要 3 個位元組。例如,GIF 文件格式就使用了這樣的色盤。
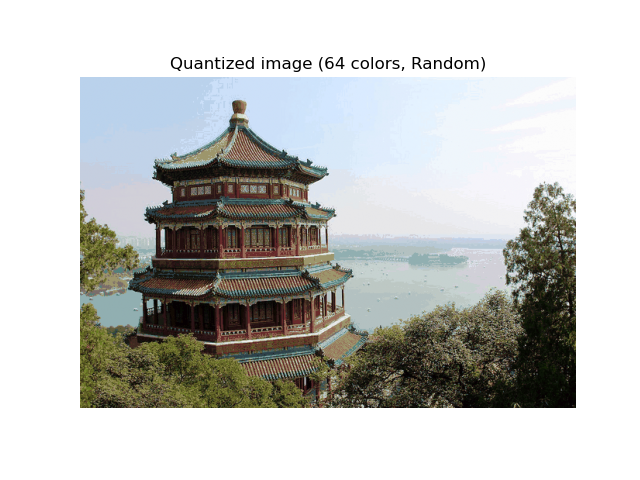
為了比較,還顯示了使用隨機碼本(隨機選取的顏色)量化的圖像。
Fitting model on a small sub-sample of the data
done in 0.028s.
Predicting color indices on the full image (k-means)
done in 0.031s.
Predicting color indices on the full image (random)
done in 0.100s.
# Authors: Robert Layton <robertlayton@gmail.com>
# Olivier Grisel <olivier.grisel@ensta.org>
# Mathieu Blondel <mathieu@mblondel.org>
#
# License: BSD 3 clause
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import load_sample_image
from sklearn.metrics import pairwise_distances_argmin
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
n_colors = 64
# Load the Summer Palace photo
china = load_sample_image("china.jpg")
# Convert to floats instead of the default 8 bits integer coding. Dividing by
# 255 is important so that plt.imshow works well on float data (need to
# be in the range [0-1])
china = np.array(china, dtype=np.float64) / 255
# Load Image and transform to a 2D numpy array.
w, h, d = original_shape = tuple(china.shape)
assert d == 3
image_array = np.reshape(china, (w * h, d))
print("Fitting model on a small sub-sample of the data")
t0 = time()
image_array_sample = shuffle(image_array, random_state=0, n_samples=1_000)
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=n_colors, random_state=0).fit(image_array_sample)
print(f"done in {time() - t0:0.3f}s.")
# Get labels for all points
print("Predicting color indices on the full image (k-means)")
t0 = time()
labels = kmeans.predict(image_array)
print(f"done in {time() - t0:0.3f}s.")
codebook_random = shuffle(image_array, random_state=0, n_samples=n_colors)
print("Predicting color indices on the full image (random)")
t0 = time()
labels_random = pairwise_distances_argmin(codebook_random, image_array, axis=0)
print(f"done in {time() - t0:0.3f}s.")
def recreate_image(codebook, labels, w, h):
"""Recreate the (compressed) image from the code book & labels"""
return codebook[labels].reshape(w, h, -1)
# Display all results, alongside original image
plt.figure(1)
plt.clf()
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Original image (96,615 colors)")
plt.imshow(china)
plt.figure(2)
plt.clf()
plt.axis("off")
plt.title(f"Quantized image ({n_colors} colors, K-Means)")
plt.imshow(recreate_image(kmeans.cluster_centers_, labels, w, h))
plt.figure(3)
plt.clf()
plt.axis("off")
plt.title(f"Quantized image ({n_colors} colors, Random)")
plt.imshow(recreate_image(codebook_random, labels_random, w, h))
plt.show()
腳本總運行時間:(0 分鐘 0.595 秒)
相關範例